Entropy Change Of System
Entropy change of system. That is a high value because of the gas and liquid molecules being formed from two more ordered solids. Assuming the system is isolated from the rest of the world. 3 If the system is in contact with a thermostat at temperature T then NVTremain constants 2.
According to Clausius the entropy was defined via the change in entropy S of a system. Entropy is a factor of state function ie its value does not dependent on the pathway of the. By the system the entropy of the system depends upon the heat absorbed reversibly.
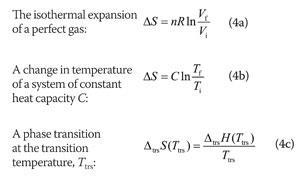
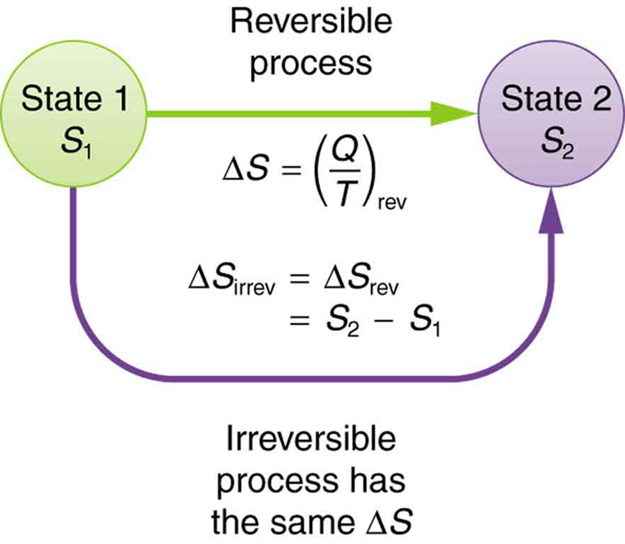
The entropy change of a system in a process is equal to the amount of heat transferred to it in a reversible manner divided by the temperature at which the transfer takes place. For an isolated system the second term integral is always zero because it does not exchange heat with its surroundings. We calculate entropy change for isobaric processes in a similar way to isochoric processes.
Adding these two entropy changes together yields a total entropy change of Δ H T Δ S 1 T Δ H T Δ S 1 T Δ G where Δ G is known as the. In this case however heat is transferred to the system from the surroundings so that The heat transferred from the surroundings however is equal to the heat received by the system. Continue reading Calculate the change in the entropies of the system and.
Consider now an irreversible process in which the system absorbs an amount dq irrev of heat and on from state A to state B. When the system eventually settle down to the new equilibrium state without constraint the new entropy is SNVE max SNVE. Therefore entropy change of the system at an absolute temperature T will be 𝛥 29 Similarly the entropy change of the surrounding will be 𝛥 30 The total entropy of the isolated system system surrounding will be 𝛥.
For a system the energy associated with entropy can be calculated as the degree of disorder or the randomness of the system. The entropy is a state variable so the entropy change of the system is the same as before. Here Q is the energy transferred as heat to or from the system during the process and T is the temperature of the system in kelvins during the process.
Under conditions of constant pressure and temperature the former is the energy released by the system into its environment traditionally represented by ΔH times 1 T and the latter is Δ S. A system with a great degree of disorderliness has more entropy.
The entropy change of the surroundings can be calculated by the equation dS_surfracdqT_sur regardless of the path irreversible or reversible.
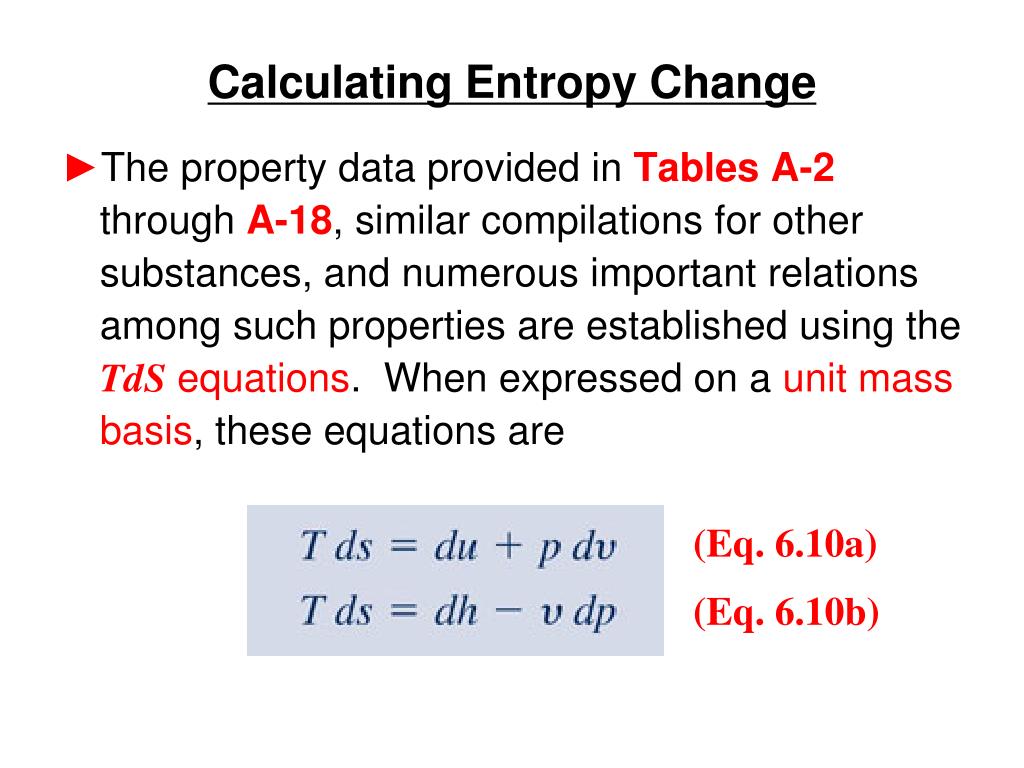
Meaning of Entropy. The entropy change of a system in a process is equal to the amount of heat transferred to it in a reversible manner divided by the temperature at which the transfer takes place. The entropy is a state variable so the entropy change of the system is the same as before. We calculate isochoric entropy change by Reversible heatingcooling at constant P reversible isobaric. Entropy change what you end up with - what you started with. What is Entropy Change. Physical chemistry - Entropy change of surroundings and system - Chemistry Stack Exchange. The change in entropy S when an amount of heat Q is added to it by a reversible process at constant temperature is given by. Total entropy at the end 214 2699 3538 J K-1 mol-1.
Assuming it is produced as BaCl 2 the entropy change for the system is 591J K-1 mol-1. When a system cools its entropy decreases. Change in Entropy of a System. The entropy change of the system is the amount of energy of the system. Entropy change can be defined as the change in the state of disorder of a thermodynamic system that is associated with the conversion of heat or enthalpy into work. When heat is supplied to a system the disorder increases. SackurTetrode entropy the entropy of a monatomic classical ideal gas determined via quantum considerations.











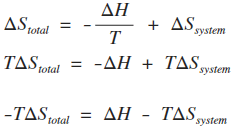














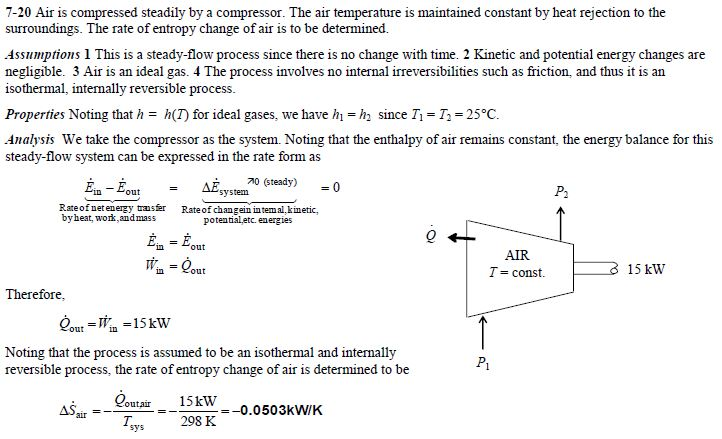







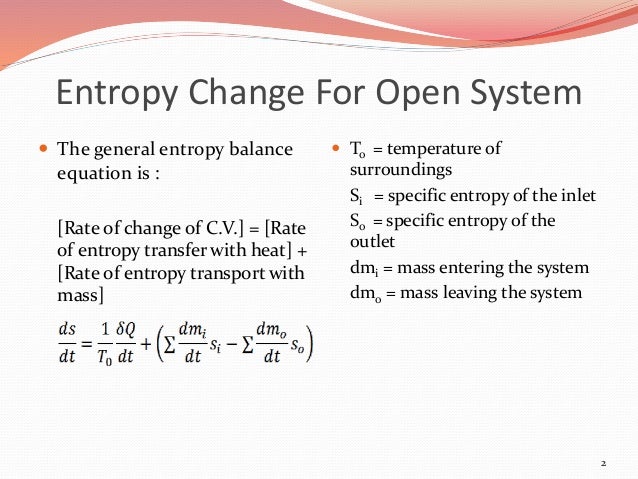


Post a Comment for "Entropy Change Of System"